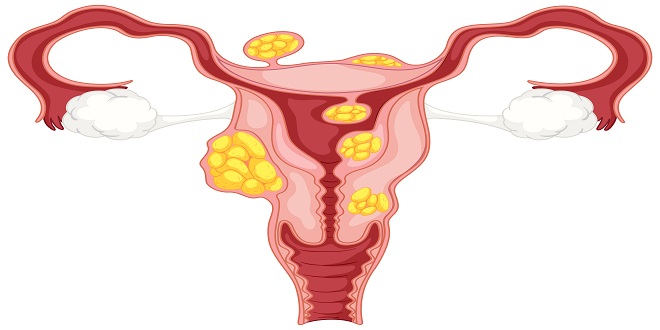
Do you experience unusual vaginal bleeding or pelvic pain? You could have uterine fibroids, which are non-cancerous tumours of the uterus. Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous uterine growths that can appear during pregnancy. Fibroids, also known as uterine myomas, are among the most prevalent tumours of the female reproductive system. Fibroids can become significant in some women and cause severe symptoms such as irregular menstruation, heavy periods, and abdominal pain. Gynaecology doctors in Hyderabad treat female health issues such as uterine fibroids, pregnancy, menstrual cycle, fertility issues, and childbirth.
Uterine fibroids can range in size from undetectable seedlings to bulky masses that can distort and lead to uterine enlargement. Multiple fibroids can cause the uterus to expand to the point where it can reach the rib cage and add weight to it. If you’ve been having pelvic pain and discomfort and are beginning to wonder what the symptoms of uterine fibroids are, keep reading.
What exactly are uterine fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are growths composed of muscle and connective tissue from the uterine wall. These growths are not usually cancerous (benign). In your pelvis, uterus is an upside-down pear-shaped organ and uterus is roughly the size of a lemon. During pregnancy, it is the location where a baby grows and develops.
Uterine Fibroid Symptoms
The symptoms of uterine fibroids differ. Some women have no symptoms, while others have abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, and pregnancy complications.
Unusual Bleeding
Heavy and prolonged bleeding is a common presenting complaint of women with uterine fibroids. However, the bleeding pattern can change.
Heavy Menstrual Bleeding – 60% of women with uterine fibroids experience heavy menstrual bleeding. This bleeding can cause significant blood loss, necessitating iron supplements or, in some cases, a blood transfusion.
More Frequent Bleeding: Women also note troubles with bleeding between periods; some even have full periods that occur more frequently than in a typical cycle.
Pelvic Dissatisfaction
Because fibroids can take up space inside the pelvis, symptoms such as organ compression may occur. Urinary Tract Issues – The bladder sits atop the uterus. A fibroid can press against the bladder, making it difficult to empty. This can result in the following:
- Increased frequency of urination
- Incontinence of the bladder
- Urination difficulties
- Hydronephrosis is a blockage of the urine flow that can harm the kidneys.
Bowel Movement Disorders – The rectum is the large intestine containing stool before a bowel movement. It is located behind the uterus. A fibroid can compress the rectum and cause bowel movements to be complex, resulting in symptoms such as:
- Constipation
- Tenesmus is a condition in which you feel the need to urinate but cannot.
- Pelvic Mass – Some women may experience a large lump or swelling in their lower abdomen. This is possible with large uterine fibroids.
Pelvic Pain – While fibroid growth may not be a problem during pregnancy, pain associated with uterine fibroids can be a problem. As a result, up to 15% of pregnant women are hospitalized for pain management.
Delivery Complications: These can include premature labour, bleeding around the placenta or the sac that contains the unborn baby, problems with the baby’s position, and heavy bleeding after delivery. Going into labour too soon, bleeding around the placenta or the sac containing the unborn baby, problems with the baby’s position, and excessive bleeding after delivery are all complications.
What factors contribute to uterine fibroids?
Many doctors are still unable to determine the cause of uterine fibroids, but research and clinical experience point to the following factors:
Genetical Changes – Many fibroids are associated with gene changes that differ from those found in normal uterine muscle cells. Estrogenic and progesterone are hormones that control the development of the uterine lining during menstrual cycles, resulting in pregnancy preparation, and which later appear to promote the growth of fibroids in the urinary tract.
Other growth factors – Substances and fluids that aid tissue maintenance, such as insulin-like growth factors, may influence fibroid growth.
Extracellular matrix (ECM) – ECM is a material that helps cells adhere to one another. Fibroids become fibrous when their ECM levels rise. ECM also stores growth factors or hormones, which cause biochemical effects in the body’s cells. Feel free to visit to know more about – whealthtips
Conclusion
Uterine fibroids are a common symptom many faces at some point in their lives. In some cases, fibroids are so tiny that they do not cause any symptoms. However, Fibroids can also cause difficult symptoms at times. If you are experiencing any discomfort or pain, contact your healthcare provider. Fibroids can be treated, and your symptoms can often be alleviated.
 Isaiminia World Breaking News & Top Stories
Isaiminia World Breaking News & Top Stories